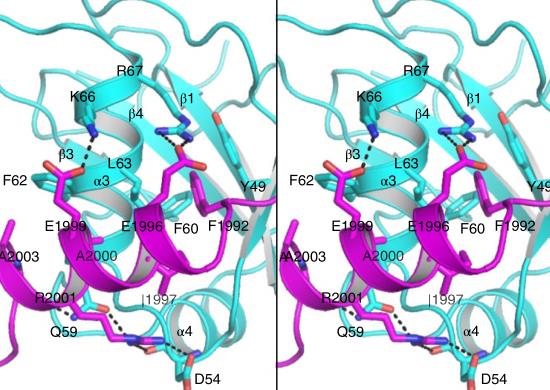
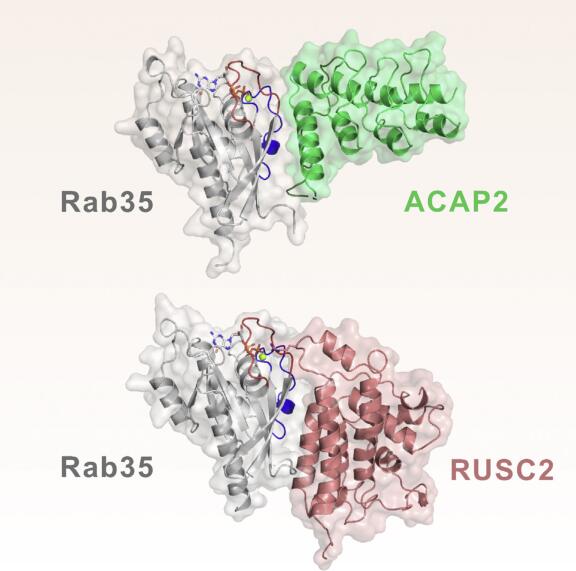
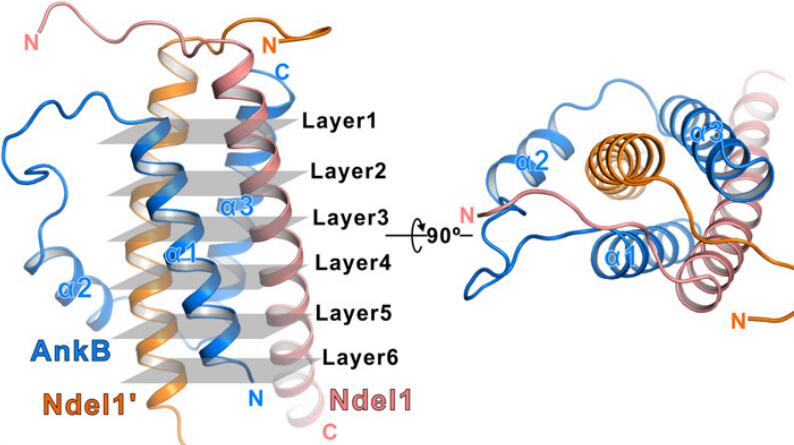
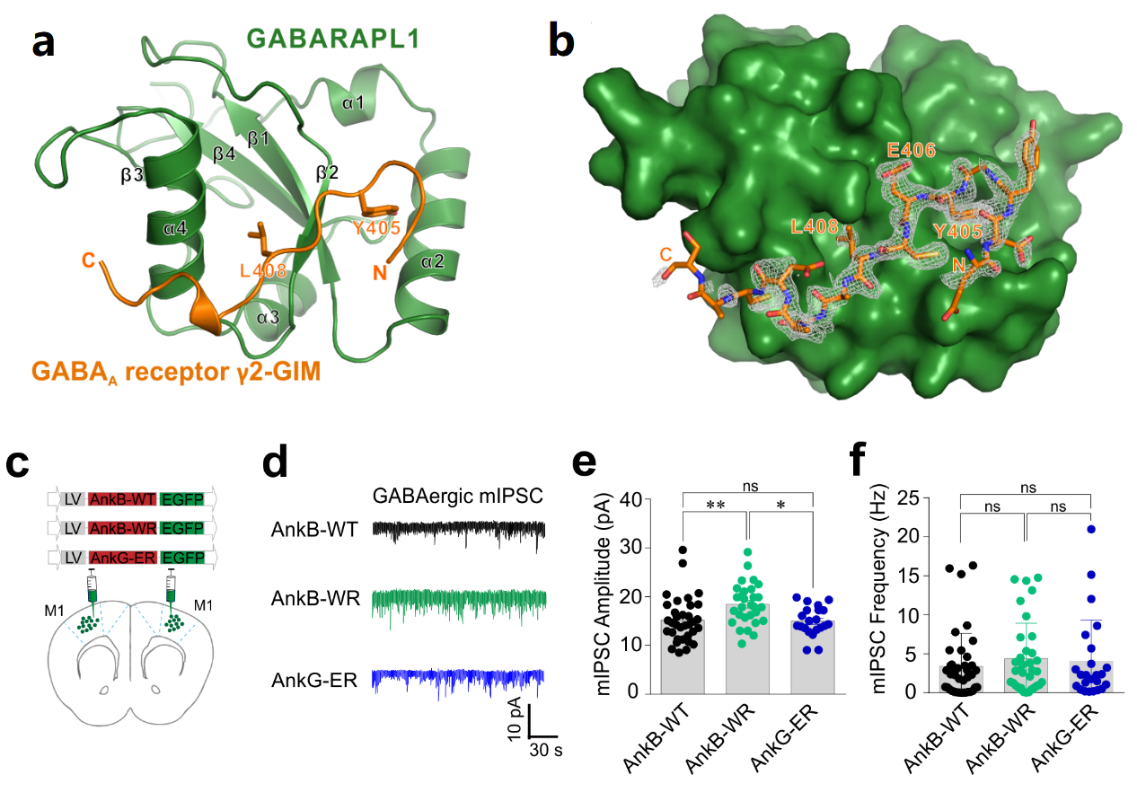
Current Hits
GABAA receptors are the main inhibitory neurotransmitter receptors in the central nervous system, which can inhibit the excitability of nerves by mediating the influx of chloride ions outside nerve cells. The location and distribution of GABAA receptors on nerve cell membranes play an important role in regulating the generation and conduction of nerve signals. A large number of studies have shown that the imbalance of GABAA receptor distribution in the cell membrane is closely related to the occurrence of neurological diseases, including a variety of neurodevelopmental and signal conduction diseases, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and autism; chronic nerves System diseases, such as anxiety, depression, and insomnia. In addition, GABAA receptors are also important drug targets for central nervous system diseases. Therefore, there is no doubt that the dynamic regulation of GABAA receptors plays an important role in the nervous system, and it has always been the focus of research at home and abroad. However, there are still a lot of blanks in the research on the molecular mechanism of GABAA receptor transport regulation on the cell membrane.